
Denmark
God's help, the love of the people, Denmark's
strength!
History
Geography
Economy
Population
Interesting facts
Denmark has a developed mixed economy
that is classed as a high-income economy by the World
Bank. In 2017, it ranked 16th in the world in terms of
gross national income (PPP) per capita and 10th in nominal
GNI per capita. Denmark's economy stands out as one of the
most free in the Index of Economic Freedom and the
Economic Freedom of the World. It is the 10th most
competitive economy in the world, and 6th in Europe,
according to the World Economic Forum in its Global
Competitiveness Report 2018. Lego was also created in
Denmark. Like other Nordic countries, Denmark has adopted
the Nordic Model, which combines free market capitalism
with a comprehensive welfare state and strong worker
protection. As a result of its acclaimed "flexicurity"
model, Denmark has the freest labour market in Europe,
according to the World Bank. Denmark has considerably
large deposits of oil and natural gas in the North Sea and
ranks as number 32 in the world among net exporters of
crude oil and was producing 259,980 barrels of crude oil a
day in 2009. Denmark is a long-time leader in wind power:
In 2015 wind turbines provided 42.1% of the total
electricity consumption. In May 2011 Denmark derived 3.1%
of its gross domestic product from renewable (clean)
energy technology and energy efficiency, or around €6.5
billion ($9.4 billion). Denmark is connected by electric
transmission lines to other European countries. Denmark
has a long tradition of scientific and technological
invention and engagement, and has been involved
internationally from the very start of the scientific
revolution. In current times, Denmark is participating in
many high-profile international science and technology
projects, including CERN, ITER, ESA, ISS and E-ELT.
Denmark was ranked 9th in the Global Innovation Index in
2021, down from 6th in 2020 and from 7th in 2019.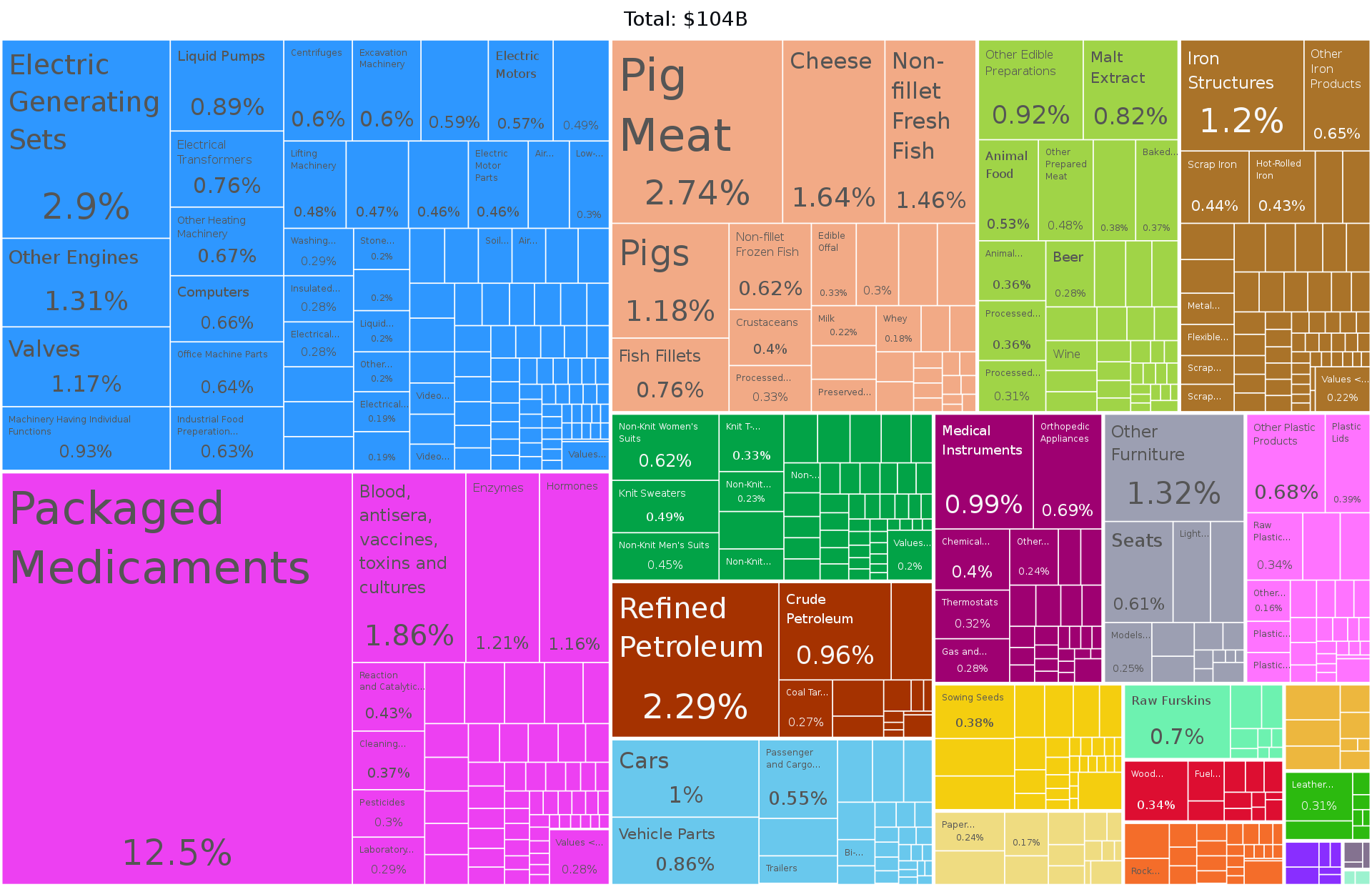
Significant investment has been made in
building road and rail links between regions in Denmark,
most notably the Great Belt Fixed Link, which connects
Zealand and Funen. It is now possible to drive from
Frederikshavn in northern Jutland to Copenhagen on eastern
Zealand without leaving the motorway. The main railway
operator is DSB for passenger services and DB Cargo for
freight trains. The railway tracks are maintained by
Banedanmark. The North Sea and the Baltic Sea are
intertwined by various, international ferry links.
Construction of the Fehmarn Belt Fixed Link, connecting
Denmark and Germany with a second link, will start in
2015.